
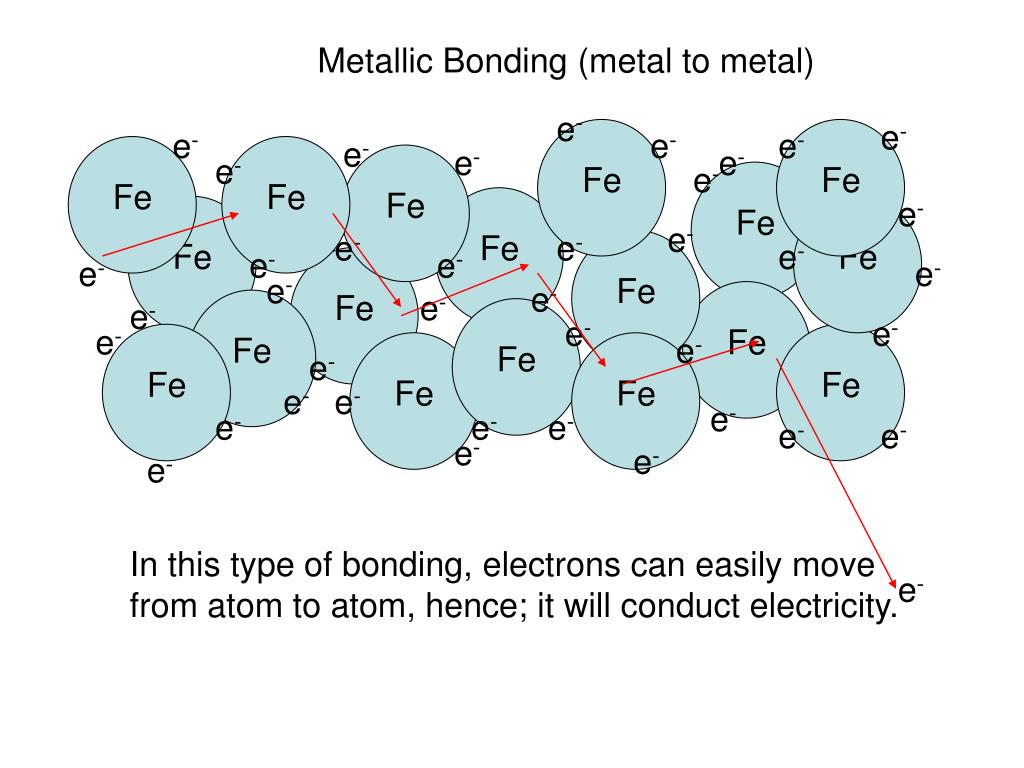
(free moving) and act as charge carriers which help to conduct electricity and heat. These ‘sea’ of delocalised electrons are mobile The valence (outermost shell) electrons delocalised into the empty spaces (‘sea’) and are able to move freely within the metal lattice. ‘Sea’ of delocalised electrons surrounding the positively charged metal ions in the giant metallic lattice structure 4) Good conductors of electricity (and heat) As such, pure metals are known to be soft, malleable and ductile. When a force is applied to a metal, the layers of metal atoms can slide past each other. In pure metals, same size atoms are packed closely together in a regular pattern. Ductility refers to the ability to be stretched or drawn into wires without breaking. Malleability refers to the ability to be beaten or hammered into shapes without breaking. As such, there is large number of atoms per unit volume i.e. Physical Properties of Metals 1) Usually have high densitiesĪtoms in a metal are packed tightly in layers and are held together by strong metallic bonds. These physical properties can be easily explained by looking at the structures of metal. Good conductors of electricity (and heat).Usually have high melting points and boiling points i.e.In general, metals have the following physical properties:

Titanium and zirconium are also commonly used for making aircraft and space shuttle parts. Copper is widely used in metal wires and cables.
Metals are commonly being used in our everyday lives.įor example, silver and gold are commonly used as jewellery because of their shiny appearance. Is Iron Man made of a Pure Metal or An Alloy?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
